Table of Content
To be exempt from capital gains tax on the sale of your home, the home must be considered your principal residence based on Internal Revenue Service rules. These rules state that you must have occupied the residence for at least 24 months of the last five years. You could owe capital gains tax if you sell a home that has appreciated in value because it is a capital asset. However, thanks to the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997, most homeowners are exempt from needing to pay it. There's no limit to the number of times you can claim the exclusion. The property you buy must be of the same “character and class” as the property sold.

If you pay these amounts as the buyer, include them in your cost basis of the property. If you have gain that can’t be excluded, you must generally report it on Form 8949, Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets, and Schedule D , Capital Gains and Losses. Report the sale on Part I or Part II of Form 8949 as a short-term or long-term transaction, depending on how long you owned the home.
Main navigation
Apply for an online payment agreement (IRS.gov/OPA) to meet your tax obligation in monthly installments if you can’t pay your taxes in full today. Once you complete the online process, you will receive immediate notification of whether your agreement has been approved. ▶ Tips and links to help you determine if you qualify for tax credits and deductions. If you granted someone an option to buy your home and it expired in the year of sale, report the amount you received for the option as ordinary income. You may be able to deduct them on your tax return for the year of sale. Divide the number of days you owned the property during the year of sale, not counting the date of sale, by 365 .
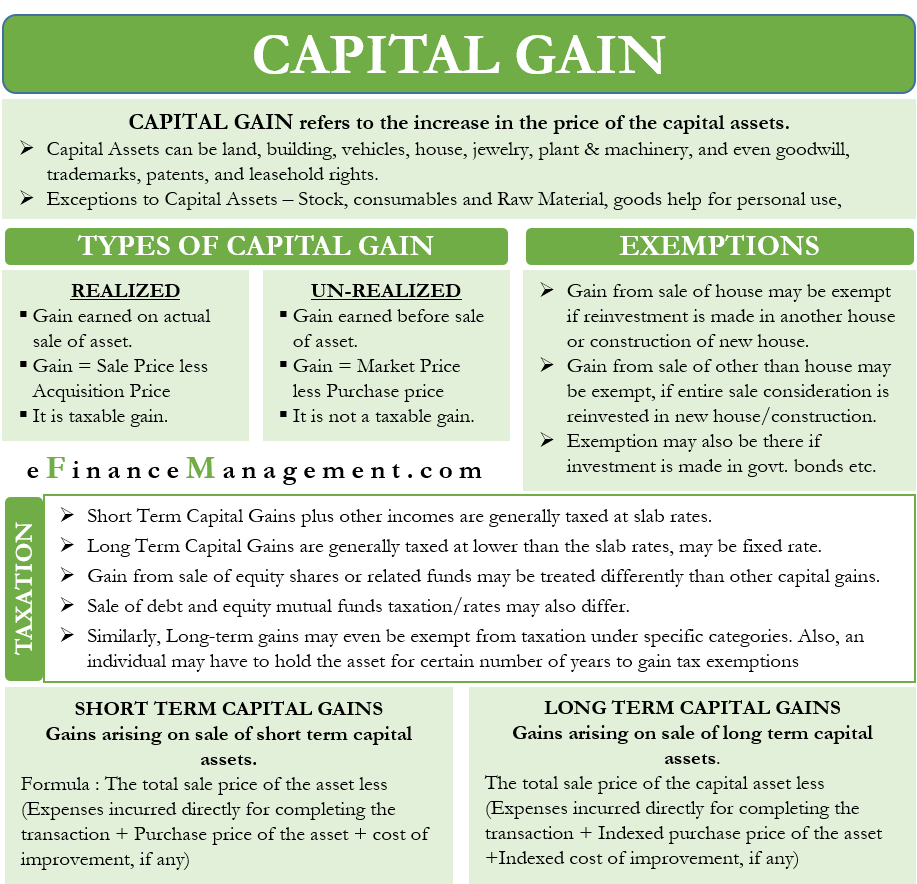
When you sell your home, the IRS allows one major form of capital gains break. It’s called the home sale exclusion, and it allows you to deduct a significant amount of the profit from your home sale to minimize or avoid capital gains taxes. If you’re selling an investment property, you can use the process known as a “like-kind” exchange to lower your tax burden, but this process only applies to investment and rental properties. A 1031 exchange allows you to defer paying capital gains taxes when you sell a property and reinvest the proceeds in another.
Suspension of the Five-Year Test Period
If the FMV of the property at the time the donor made the gift is less than the donor's adjusted basis, your adjusted basis depends on whether you have a gain or loss when you dispose of the property. You report as ordinary income on line 1 of Form 1040, U.S. Your employer should report the ordinary income to you as wages in box 1 of Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement.

Transfer of home, Transfer of your home to a spouse or an ex-spouse. Use the Offer in Compromise Pre-Qualifier to see if you can settle your tax debt for less than the full amount you owe. For more information on the Offer in Compromise program, go to IRS.gov/OIC. Approve or reject authorization requests from tax professionals. Make a payment or view 5 years of payment history and any pending or scheduled payments.
Publication 523 ( , Selling Your Home
This tool lets your tax professional submit an authorization request to access your individual taxpayer IRS online account. The Tax Withholding Estimator (IRS.gov/W4app) makes it easier for everyone to pay the correct amount of tax during the year. The tool is a convenient, online way to check and tailor your withholding. It’s more user-friendly for taxpayers, including retirees and self-employed individuals. Armed Forces and qualified veterans may use MilTax, a free tax service offered by the Department of Defense through Military OneSource. For more information go to MilitaryOneSource (MilitaryOneSource.mil/Tax).
Use this worksheet only if no automatic disqualifications apply, and take all exceptions into account. You began to experience significant financial difficulty maintaining the home. An event is determined to be an unforeseeable event in IRS published guidance. The above is true of your spouse, a co-owner of the home, or anyone else for whom the home was his or her residence. Either of the above is true of your spouse, a co-owner of the home, or anyone else for whom the home was his or her residence. If you didn’t meet the Eligibility Test, then your home isn’t eligible for the maximum exclusion, but you should continue to Does Your Home Qualify for a Partial Exclusion of Gain.
Use 1031 Exchanges to Avoid Taxes
Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, up to $750,000 of mortgage interest on a principal residence or vacation home can be deducted. However, if a property is solely used as an investment property, it does not qualify for the capital gains exclusion. The IRS approaches taxes on these gains in differing ways, depending on whether the investor held the assets, either short or long term. Investors can deduct your cost basis or original purchase price to determine the capital gains. You can subtract the cost basis and any costs of improvements from the profit from the capital gains. If you sell below-market to a relative or friend, the transaction may subject the recipient to taxes on the difference, which the IRS may consider a gift.
First and most importantly, hold the property for at least two years! Section 121 exclusion only kicks in after two years of ownership. TAS works to resolve large-scale problems that affect many taxpayers. If you know of one of these broad issues, report it to them at IRS.gov/SAMS. The IRS uses the latest encryption technology to ensure that the electronic payments you make online, by phone, or from a mobile device using the IRS2Go app are safe and secure. Paying electronically is quick, easy, and faster than mailing in a check or money order.
If you owned the home for more than one year, which you did, the gain is a long term capital gain. You need to use a Schedule D to calculate the gain and include the gain on your Form 1040. The tax rate on long term capital gains is generally lower than your regular tax rate.

You may have ordinary income if the option price was below the stock's fair market value at the time the option was granted. Let’s say your replacement property is a bit cheaper than your relinquished property. You’ll likely be liable for capital gains taxes on the difference. Another option for deferring capital gains taxes is to do a tax-deferred exchange, called a Section 1031 exchange by the IRS. Section 121 is a provision of the tax code that allows home sellers to exclude a certain amount of their gains from taxation. It applies if they’re selling a primary residence and meet other requirements.
Section 121 is a provision of the tax code that allows home sellers to exclude $250,000 or $500,000 of their capital gains from taxation, depending on their filing status. If you're selling a primary resilience that you've owned and lived in for at least two of the past five years, you likely qualify for this exclusion. Tax-loss harvesting, also known as tax-loss selling, allows you to offset capital gains from one property sale against losses from another. You can consider this strategy if you’re selling a house for a gain and have another property that has depreciated in value. First, you can only exclude capital gains from the period when you actually lived in the house as your primary residence. If you rented out the home for three years and then moved in for two years, only 40% of the gain is eligible for exclusion.
The home sale exclusion does not apply to investment or rental properties. This must be a home that you live in and it cannot be a second home. You should note that you can only have one legal primary residence at a time, meaning that you can only apply the home sale exclusion to one sale at a time.